一、安装helm工具
...大约 10 分钟
一、安装helm工具
(1)下载软件包
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.8.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
(2)解压并拷贝文件位置
tar -zxvf helm-v3.8.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
这里需要注意的是将 /usr/local/bin 添加到环境变量中
二、配置chart存储库
(1)添加chart存储库
helm repo add gitlab https://charts.gitlab.io
(2)验证源
helm repo list
(3)查询可安装的gitlab-runner chart
helm search repo -l gitlab/gitlab-runner
然后查询gitlab的版本,根据gitlab的版本选择gitlab-runner的版本。比如这里查询到gitlab的版本是14.9.0,runner选择0.39.0
helm fetch gitlab/gitlab-runner --version=0.39.0
三、编辑配置文件
(1)首先解压文件
tar -zxvf gitlab-runner-0.39.0.tgz
(2)编辑配置文件
cd gitlab-runner
vi values.yaml
然后根据实际需要配置文件
四、部署Chart
使用如下命令部署
cd ..
kubectl create namespace gitlab-runner
helm install gitlab-runner --namespace gitlab-runner ./gitlab-runner
若后续更新了配置文件,则使用如下命令更新即可
helm upgrade gitlab-runner --namespace gitlab-runner ./gitlab-runner
至此即可在gitlab上看到runner了 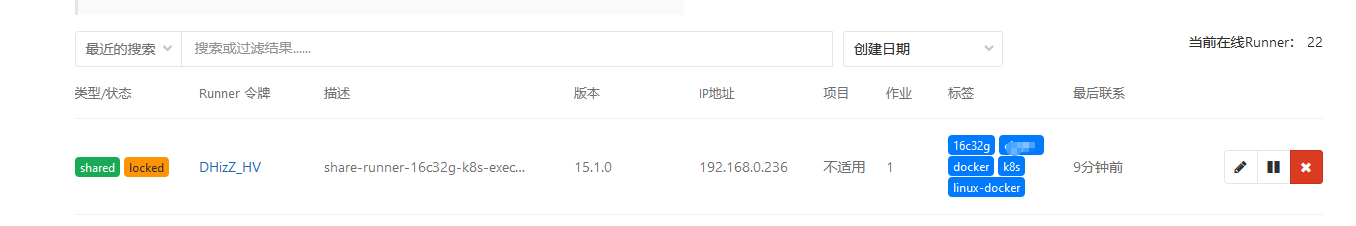
五、一份已经配置好的values文件
values.yaml
## GitLab Runner Image
##
## By default it's using registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner:alpine-v{VERSION}
## where {VERSION} is taken from Chart.yaml from appVersion field
##
## DEPRECATED: Setting `image: registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner:alpine-v11.6.0` is deprecated
##
## ref: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner/container_registry/29383?orderBy=NAME&sort=asc&search[]=alpine-v&search[]=
##
## Note: If you change the image to the ubuntu release
## don't forget to change the securityContext;
## these images run on different user IDs.
##
image:
registry: registry.gitlab.com
image: gitlab-org/gitlab-runner
# tag: alpine-v11.6.0
## Specify a imagePullPolicy for the main runner deployment
## 'Always' if imageTag is 'latest', else set to 'IfNotPresent'
##
## Note: it does not apply to job containers launched by this executor.
## Use `pull_policy` in [runners.kubernetes] to change it.
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images/#pre-pulled-images
##
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
## Specifying ImagePullSecrets on a Pod
## Kubernetes supports specifying container image registry keys on a Pod.
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images/#specifying-imagepullsecrets-on-a-pod
##
# imagePullSecrets:
# - name: "image-pull-secret"
## Timeout, in seconds, for liveness and readiness probes of a runner pod.
# probeTimeoutSeconds: 1
## How many runner pods to launch.
##
## Note: Using more than one replica is not supported with a runnerToken. Use a runnerRegistrationToken
## to create multiple runner replicas.
# replicas: 1
## How many old ReplicaSets for this Deployment you want to retain
# revisionHistoryLimit: 10
## The GitLab Server URL (with protocol) that want to register the runner against
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/commands/README.html#gitlab-runner-register
##
gitlabUrl: http://gitlabd.xxxxx.com/
## The Registration Token for adding new Runners to the GitLab Server. This must
## be retrieved from your GitLab Instance.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/ci/runners/README.html
##
runnerRegistrationToken: "xxxxxxxxxx"
## The Runner Token for adding new Runners to the GitLab Server. This must
## be retrieved from your GitLab Instance. It is token of already registered runner.
## ref: (we don't yet have docs for that, but we want to use existing token)
##
# runnerToken: ""
#
## Unregister runner before termination
##
## Updating the runner's chart version or configuration will cause the runner container
## to be terminated and created again. This may cause your GitLab instance to reference
## non-existant runners. Un-registering the runner before termination mitigates this issue.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/commands/README.html#gitlab-runner-unregister
##
## Please set unregisterRunners to false if you set unregisterRunner to true as only
## one preStop action is supported.
##
# unregisterRunner: true
## Unregister all runners before termination
##
## Updating the runner's chart version or configuration will cause the runner container
## to be terminated and created again. This may cause your Gitlab instance to reference
## non-existant runners. Un-registering the runner before termination mitigates this issue.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/commands/README.html#gitlab-runner-unregister
##
# unregisterRunners: true
## When stopping the runner, give it time to wait for its jobs to terminate.
##
## Updating the runner's chart version or configuration will cause the runner container
## to be terminated with a graceful stop request. terminationGracePeriodSeconds
## instructs Kubernetes to wait long enough for the runner pod to terminate gracefully.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/commands/#signals
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 3600
## Set the certsSecretName in order to pass custom certficates for GitLab Runner to use
## Provide resource name for a Kubernetes Secret Object in the same namespace,
## this is used to populate the /home/gitlab-runner/.gitlab-runner/certs/ directory
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/tls-self-signed.html#supported-options-for-self-signed-certificates
##
# certsSecretName:
## Configure the maximum number of concurrent jobs
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-global-section
##
concurrent: 10
## Defines in seconds how often to check GitLab for a new builds
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-global-section
##
checkInterval: 30
## Configure GitLab Runner's logging level. Available values are: debug, info, warn, error, fatal, panic
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-global-section
##
# logLevel:
## Configure GitLab Runner's logging format. Available values are: runner, text, json
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-global-section
##
# logFormat:
## Configure GitLab Runner's Sentry DSN.
## ref https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-global-section
##
# sentryDsn:
## A custom bash script that will be executed prior to the invocation
## gitlab-runner process
#
#preEntrypointScript: |
# echo "hello"
## Specify whether the runner should start the session server.
## Defaults to false
## ref:
##
## When sessionServer is enabled, the user can either provide a public publicIP
## or either rely on the external IP auto discovery
## When a serviceAccountName is used with the automounting to the pod disable,
## we recommend the usage of the publicIP
sessionServer:
enabled: false
# annotations: {}
# timeout: 1800
# internalPort: 8093
# externalPort: 9000
# publicIP: ""
# loadBalancerSourceRanges:
# - 1.2.3.4/32
## For RBAC support:
rbac:
create: true
## Define specific rbac permissions.
## DEPRECATED: see .Values.rbac.rules
# resources: ["pods", "pods/exec", "secrets"]
# verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "patch", "delete"]
## Define list of rules to be added to the rbac role permissions.
## Each rule supports the keys:
## - apiGroups: default "" (indicates the core API group) if missing or empty.
## - resources: default "*" if missing or empty.
## - verbs: default "*" if missing or empty.
rules: []
# - resources: ["configmaps", "pods", "pods/attach", "secrets", "services"]
# verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "patch", "delete"]
# - apiGroups: [""]
# resources: ["pods/exec"]
# verbs: ["create", "patch", "delete"]
## Run the gitlab-bastion container with the ability to deploy/manage containers of jobs
## cluster-wide or only within namespace
clusterWideAccess: false
## Use the following Kubernetes Service Account name if RBAC is disabled in this Helm chart (see rbac.create)
##
# serviceAccountName: default
## Specify annotations for Service Accounts, useful for annotations such as eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn
##
## ref: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/specify-service-account-role.html
##
# serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
## Use podSecurity Policy
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
podSecurityPolicy:
enabled: false
resourceNames:
- gitlab-runner
## Specify one or more imagePullSecrets used for pulling the runner image
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/#add-imagepullsecrets-to-a-service-account
##
# imagePullSecrets: []
## Configure integrated Prometheus metrics exporter
##
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/monitoring/#configuration-of-the-metrics-http-server
##
metrics:
enabled: false
## Define a name for the metrics port
##
portName: metrics
## Provide a port number for the integrated Prometheus metrics exporter
##
port: 9252
## Configure a prometheus-operator serviceMonitor to allow autodetection of
## the scraping target. Requires enabling the service resource below.
##
serviceMonitor:
enabled: false
## Provide additional labels to the service monitor ressource
##
## labels: {}
## Define a scrape interval (otherwise prometheus default is used)
##
## ref: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#scrape_config
##
# interval: ""
## Specify the scrape protocol scheme e.g., https or http
##
# scheme: "http"
## Supply a tls configuration for the service monitor
##
## ref: https://github.com/helm/charts/blob/master/stable/prometheus-operator/crds/crd-servicemonitor.yaml
##
# tlsConfig: {}
## The URI path where prometheus metrics can be scraped from
##
# path: "/metrics"
## A list of MetricRelabelConfigs to apply to samples before ingestion
##
## ref: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#metric_relabel_configs
##
# metricRelabelings: []
## A list of RelabelConfigs to apply to samples before scraping
##
## ref: https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#relabel_config
##
## relabelings: []
## Configure a service resource e.g., to allow scraping metrics via
## prometheus-operator serviceMonitor
service:
enabled: false
## Provide additonal labels for the service
##
# labels: {}
## Provide additonal annotations for the service
##
# annotations: {}
## Define a specific ClusterIP if you do not want a dynamic one
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#choosing-your-own-ip-address
##
# clusterIP: ""
## Define a list of one or more external IPs for this service
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#external-ips
##
# externalIPs: []
## Provide a specific loadbalancerIP e.g., of an external Loadbalancer
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#loadbalancer
##
# loadBalancerIP: ""
## Provide a list of source IP ranges to have access to this service
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#aws-nlb-support
##
# loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
## Specify the service type e.g., ClusterIP, NodePort, Loadbalancer or ExternalName
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#publishing-services-service-types
##
type: ClusterIP
## Specify the services metrics nodeport if you use a service of type nodePort
##
# metrics:
## Specify the node port under which the prometheus metrics of the runner are made
## available.
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#nodeport
##
# nodePort: ""
## Provide a list of additional ports to be exposed by this service
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#defining-a-service
##
# additionalPorts: []
## Configuration for the Pods that the runner launches for each new job
##
runners:
# runner configuration, where the multi line strings is evaluated as
# template so you can specify helm values inside of it.
#
# tpl: https://helm.sh/docs/howto/charts_tips_and_tricks/#using-the-tpl-function
# runner configuration: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html
config: |
[[runners]]
[runners.kubernetes]
namespace = "{{.Release.Namespace}}"
image = "ubuntu:16.04"
## Which executor should be used
##
# executor: kubernetes
## Default container image to use for builds when none is specified
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# image: ubuntu:16.04
## Specify one or more imagePullSecrets
##
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# imagePullSecrets: []
## Specify the image pull policy: never, if-not-present, always. The cluster default will be used if not set.
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# imagePullPolicy: ""
## Defines number of concurrent requests for new job from GitLab
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-runners-section
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# requestConcurrency: 1
## Specify whether the runner should be locked to a specific project: true, false. Defaults to true.
##
# locked: true
## Specify the tags associated with the runner. Comma-separated list of tags.
##
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/runners/configure_runners.html#use-tags-to-control-which-jobs-a-runner-can-run
##
tags: "16c32g,k8s,docker,linux-docker,cidana"
## Specify the name for the runner.
##
name: "share-runner-16c32g-k8s-execute"
## Specify the maximum timeout (in seconds) that will be set for job when using this Runner
##
# maximumTimeout: ""
## Specify if jobs without tags should be run.
## If not specified, Runner will default to true if no tags were specified. In other case it will
## default to false.
##
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/runners/configure_runners.html#set-a-runner-to-run-untagged-jobs
##
# runUntagged: true
## Specify whether the runner should only run protected branches.
## Defaults to false.
##
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/runners/configure_runners.html#prevent-runners-from-revealing-sensitive-information
##
# protected: true
## Run all containers with the privileged flag enabled
## This will allow the docker:dind image to run if you need to run Docker
## commands. Please read the docs before turning this on:
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/executors/kubernetes.html#using-dockerdind
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# privileged: false
## The name of the secret containing runner-token and runner-registration-token
# secret: gitlab-runner
## Namespace to run Kubernetes jobs in (defaults to the same namespace of this release)
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# namespace:
## The amount of time, in seconds, that needs to pass before the runner will
## timeout attempting to connect to the container it has just created.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/executors/kubernetes.html
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# pollTimeout: 180
## Set maximum build log size in kilobytes, by default set to 4096 (4MB)
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-runners-section
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# outputLimit: 4096
## Distributed runners caching
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/autoscale.html#distributed-runners-caching
##
## If you want to use s3 based distributing caching:
## First of all you need to uncomment General settings and S3 settings sections.
##
## Create a secret 's3access' containing 'accesskey' & 'secretkey'
## ref: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/wheres-my-secret-access-key/
##
## $ kubectl create secret generic s3access \
## --from-literal=accesskey="YourAccessKey" \
## --from-literal=secretkey="YourSecretKey"
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
##
## If you want to use gcs based distributing caching:
## First of all you need to uncomment General settings and GCS settings sections.
##
## Access using credentials file:
## Create a secret 'google-application-credentials' containing your application credentials file.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-runnerscachegcs-section
## You could configure
## $ kubectl create secret generic google-application-credentials \
## --from-file=gcs-application-credentials-file=./path-to-your-google-application-credentials-file.json
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
##
## Access using access-id and private-key:
## Create a secret 'gcsaccess' containing 'gcs-access-id' & 'gcs-private-key'.
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html#the-runnerscachegcs-section
## You could configure
## $ kubectl create secret generic gcsaccess \
## --from-literal=gcs-access-id="YourAccessID" \
## --from-literal=gcs-private-key="YourPrivateKey"
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
##
## If you want to use Azure-based distributed caching:
## First, uncomment General settings.
##
## Create a secret 'azureaccess' containing 'azure-account-name' & 'azure-account-key'
## ref: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blobs-introduction
##
## $ kubectl create secret generic azureaccess \
## --from-literal=azure-account-name="YourAccountName" \
## --from-literal=azure-account-key="YourAccountKey"
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
cache: {}
## General settings
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration and https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#using-cache-with-configuration-template
# cacheType: s3
# cachePath: "gitlab_runner"
# cacheShared: true
## S3 settings
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration and https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#using-cache-with-configuration-template
# s3ServerAddress: s3.amazonaws.com
# s3BucketName:
# s3BucketLocation:
# s3CacheInsecure: false
## GCS settings
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration and https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#using-cache-with-configuration-template
# gcsBucketName:
## S3 the name of the secret.
# secretName: s3access
## Use this line for access using gcs-access-id and gcs-private-key
# secretName: gcsaccess
## Use this line for access using google-application-credentials file
# secretName: google-application-credentials
## Use this line for access using Azure with azure-account-name and azure-account-key
# secretName: azureaccess
## Build Container specific configuration
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
builds: {}
# cpuLimit: 200m
# cpuLimitOverwriteMaxAllowed: 400m
# memoryLimit: 256Mi
# memoryLimitOverwriteMaxAllowed: 512Mi
# cpuRequests: 100m
# cpuRequestsOverwriteMaxAllowed: 200m
# memoryRequests: 128Mi
# memoryRequestsOverwriteMaxAllowed: 256Mi
## Service Container specific configuration
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
services: {}
# cpuLimit: 200m
# memoryLimit: 256Mi
# cpuRequests: 100m
# memoryRequests: 128Mi
## Helper Container specific configuration
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
helpers: {}
# cpuLimit: 200m
# memoryLimit: 256Mi
# cpuRequests: 100m
# memoryRequests: 128Mi
# image: "registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner-helper:x86_64-${CI_RUNNER_REVISION}"
## Helper container security context configuration
## Refer to https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/executors/kubernetes.html#using-security-context
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# pod_security_context:
# run_as_non_root: true
# run_as_user: 100
# run_as_group: 100
# fs_group: 65533
# supplemental_groups: [101, 102]
## Service Account to be used for runners
##
# serviceAccountName:
## If Gitlab is not reachable through $CI_SERVER_URL
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# cloneUrl:
## Specify node labels for CI job pods assignment
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# nodeSelector: {}
## Specify node tolerations for CI job pods assignment
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# nodeTolerations: {}
## Specify pod labels for CI job pods
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# podLabels: {}
## Specify annotations for job pods, useful for annotations such as iam.amazonaws.com/role
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# podAnnotations: {}
## Configure environment variables that will be injected to the pods that are created while
## the build is running. These variables are passed as parameters, i.e. `--env "NAME=VALUE"`,
## to `gitlab-runner register` command.
##
## Note that `envVars` (see below) are only present in the runner pod, not the pods that are
## created for each build.
##
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/commands/#gitlab-runner-register
##
## DEPRECATED: See https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/install/kubernetes.html#additional-configuration
# env:
# NAME: VALUE
## Specify the name of the scheduler which used to schedule runner pods.
## Kubernetes supports multiple scheduler configurations.
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/scheduling
# schedulerName: "my-custom-scheduler"
## Configure securitycontext for the main container
## ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/security-context/
##
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsNonRoot: true
privileged: false
capabilities:
drop: ["ALL"]
## Configure securitycontext valid for the whole pod
## ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/security-context/
##
podSecurityContext:
runAsUser: 100
# runAsGroup: 65533
fsGroup: 65533
# supplementalGroups: [65533]
## Note: values for the ubuntu image:
# runAsUser: 999
# fsGroup: 999
## Configure resource requests and limits
## ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/compute-resources/
##
resources: {}
# limits:
# memory: 256Mi
# cpu: 200m
# requests:
# memory: 128Mi
# cpu: 100m
## Affinity for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity
##
affinity: {}
## Node labels for pod assignment
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/
##
nodeSelector: {}
# Example: The gitlab runner manager should not run on spot instances so you can assign
# them to the regular worker nodes only.
# node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: "true"
## List of node taints to tolerate (requires Kubernetes >= 1.6)
## Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/taint-and-toleration/
##
tolerations: []
# Example: Regular worker nodes may have a taint, thus you need to tolerate the taint
# when you assign the gitlab runner manager with nodeSelector or affinity to the nodes.
# - key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/worker"
# operator: "Exists"
## Configure environment variables that will be present when the registration command runs
## This provides further control over the registration process and the config.toml file
## ref: `gitlab-runner register --help`
## ref: https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/configuration/advanced-configuration.html
##
# envVars:
# - name: RUNNER_EXECUTOR
# value: kubernetes
## list of hosts and IPs that will be injected into the pod's hosts file
hostAliases: []
# Example:
# - ip: "127.0.0.1"
# hostnames:
# - "foo.local"
# - "bar.local"
# - ip: "10.1.2.3"
# hostnames:
# - "foo.remote"
# - "bar.remote"
## Annotations to be added to manager pod
##
podAnnotations: {}
# Example:
# iam.amazonaws.com/role: <my_role_arn>
## Labels to be added to manager pod
##
podLabels: {}
# Example:
# owner.team: <my_cool_team>
## HPA support for custom metrics:
## This section enables runners to autoscale based on defined custom metrics.
## In order to use this functionality, Need to enable a custom metrics API server by
## implementing "custom.metrics.k8s.io" using supported third party adapter
## Example: https://github.com/directxman12/k8s-prometheus-adapter
##
#hpa: {}
# minReplicas: 1
# maxReplicas: 10
# metrics:
# - type: Pods
# pods:
# metricName: gitlab_runner_jobs
# targetAverageValue: 400m
## Configure priorityClassName for manager pod. See k8s docs for more info on how pod priority works:
## https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/
priorityClassName: ""
## Secrets to be additionally mounted to the containers.
## All secrets are mounted through init-runner-secrets volume
## and placed as readonly at /init-secrets in the init container
## and finally copied to an in-memory volume runner-secrets that is
## mounted at /secrets.
secrets: []
# Example:
# - name: my-secret
# - name: myOtherSecret
# items:
# - key: key_one
# path: path_one
## Additional config files to mount in the containers in `/configmaps`.
##
## Please note that a number of keys are reserved by the runner.
## See https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/charts/gitlab-runner/-/blob/main/templates/configmap.yaml
## for a current list.
configMaps: {}
## Additional volumeMounts to add to the runner container
##
volumeMounts: []
# Example:
# - name: my-volume
# mountPath: /mount/path
## Additional volumes to add to the runner deployment
##
volumes: []
# Example:
# - name: my-volume
# persistentVolumeClaim:
# claimName: my-pvc





